In the US, fast food is a $200 billion industry. The on-demand food delivery business is also growing fast and is now estimated to be a $2 billion-plus a year industry according to a new report from Edison Trends.
Let’s look at some of the biggest players and how consumers are buying meals and paying for delivery.
Biggest on-demand food delivery companies
As of Feb 2019, Edison Trends shows DoorDash has grown fastest since its 2018 snapshot of the industry.
Market share, according to the researchers, now shows DoorDash with 27.6% of the market, former leader GrubHub (26.7%), Uber Eats (25.2%), Postmates (12.1%), Others (5.9%), and Square’s Caviar (2.7%).
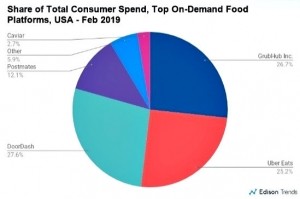
Who are these guys?
As Butch Cassidy said to the Sundance Kid, “Who are these guys?” We’ve got profiles of the top five food delivery companies.
DoorDash
San Francisco headquartered DoorDash launched in 2013 with eight rounds of funding totaling $1.4 billion to date according to Crunchbase. Sequoia Capital, Softbank, and GIC are just a few of the leading VCs backing the company. The company claims it tripled revenue in 2018 and Bloomberg reports the company earned $107 million in profits in November 2018. The service is now available in 3300 US cities and was the fastest growing in the category in 2019.
GrubHub

GrubHub started business in 2004 and is headquartered in Chicago. Its food delivery services are available in 1700 US cities and London. Now a public company (2014), GrubHub had raised $284.1 million in seven previous rounds and grew partly by acquiring a dozen companies. The company reported 2018 revenue of $1 billion, up 47% from the previous year according to CNBC. It serves 105,000 restaurants and delivered meals to more than 3.2 million customers. Investors include T Rowe Price, Lightspeed Ventures, Benchmark and DAG Ventures.
Uber Eats

Uber Eats is part of Uber’s effort to grow its business from just a high-tech taxi service. While still a private company, Uber Eats made up 17% of its business according to Bloomberg and the company sees food delivery as a key growth business suggesting it reachesd70% of the US market by the end of 2018. A 2019 IPO is planned.
Postmates

Launching in 2011, San Francisco-based Postmates provides a range of delivery and logistics services. The company has 65,000 “postmates” and operates in 44 US cities to date. It has raised $678 million in 11 rounds according to Crunchbase from investors including Tiger Global Management, Slow Ventures, Spark Capital, and Founders Fund CNBC reports. The company has earned $1.2 billion since 2017 with 165,000 drivers and 25,000 merchant partners. The private company’s share for on-demand food delivery is not segmented from other goods delivered.
Caviar

Caviar is one of the smaller delivery services companies and was founded in San Francisco in 2012. The company was acquired by payments provider Square in August 2014 for $90 million. Caviar acquired local office meal catering company Zesty in April 2018 for $20.7 million. Revenue for its food delivery business was not provided by Square but clearly, the company believes it has an inside track to small businesses who may use Square payments for their food delivery customers in the future.
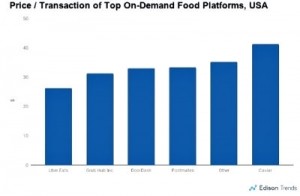
It’s interesting to note the average order size among the on-demand food delivery leaders. Caviar exceeds $40 per order because of its office employee meal focus. Uber Eats averages $27 per order while the other competitors average between $30 and $35.
Who’s growing, who’s slowing?
According to the Edison report:
“From March 2018 to February 2019, DoorDash’s monthly share of total consumer spend in the United States nearly doubled, from 15% to 28%. In comparison, the monthly share of total consumer spend of Uber Eats, Postmates, and Caviar remained roughly the same. However, GrubHub Inc. experienced an 11-percentage point loss in market share during this period, falling from 38% to 27%.”
Clearly, the recent heavy TV advertising spending by GrubHub in the past six months reflects on their competitive challenge in this growing market.

Merchants say the food delivery services help increase sales and reduce staff required for deliveries. Some merchants with DoorDash and other services still prefer to use their own delivery employees because of reported problems with unreliable drivers for the on-demand service companies.
Small local pizza and takeout restaurants aren’t the only ones benefiting from on-demand food delivery services. CNBC reports:
“McDonald’s and Uber Eats have a marquee partnership, and Yum Brands, the parent of Taco Bell, KFC and Pizza Hut, bought a 3% stake in GrubHub earlier this year.”
Analysts say the cost to merchants for the on-demand delivery service is between 15% to 25% of the increase in sales and merchants need to carefully calculate the benefits and costs. The business model works well in densely populated tier one markets and analysts expect continued growth but also much consolidation within the industry in the near future.

The payments industry is also a beneficiary of the growth of the e-commerce segment within the on-demand food delivery business. You can read more of Edison Trends’ report here.
Data charts courtesy of Edison Trends

